Most people think of sardines as old-fashioned pantry food, but the truth is far more powerful. Aside from being versatile and budget-friendly, they’re one of the healthiest foods you can easily purchase.
Sardines offer bioavailable protein, critical amino acids like taurine and arginine, and highly absorbable omega-3s, all in one bite. Their impressive nutritional profile is what makes them a foundational food that helps fight inflammation, protect your heart, and restore metabolic health.
Sardines Deliver a Nutrient Matrix That Protects Your Heart and Brain
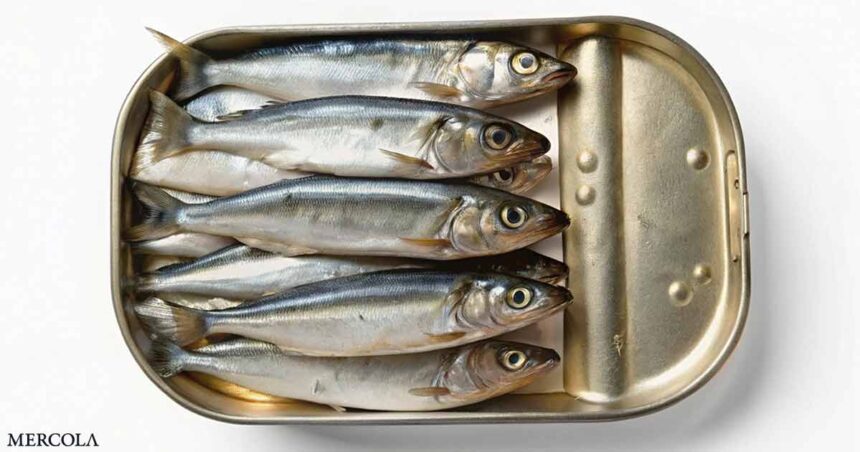
Small and fast-growing, sardines are a type of oily fish that belong to the herring family. These silvery fish, which can be distinguished by having one small dorsal fin, are found in almost every ocean in the world.1 Sardines are available fresh or canned, preserved in cans with oil, water, or sauce. They have a meaty texture and a mild, fishy flavor,2 making them a versatile ingredient for various seafood dishes.
Despite their size (they typically do not exceed 12 inches in length) sardines deliver a comprehensive matrix of nutrients that provide myriad benefits, from supporting bone health to promoting red blood cell formation. They are packed with healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and protein, all in one whole food. To give you a clearer idea, here’s what you’ll get from a 100-gram serving of sardines,3 as detailed by News-Medical.net:4
• Protein (24 grams) — The high-quality, bioavailable protein in sardines provides fuel for your muscles, supporting repair, growth, and energy. Sardines also provide you with taurine and arginine, which are essential amino acids that support heart and blood pressure health, as well as boost your antioxidant systems.
• Vitamin B12 (8.9 micrograms) — This nutrient helps improve your energy levels and supports red blood cell production. It’s also essential for brain health. Other vitamins found in this food are vitamins E and D (sardines are actually one of the few food sources of this nutrient5).
• Calcium (382 mg) — Sardines are a good dairy alternative because of their high calcium content (for context, an 8-ounce cup of milk contains 300 mg of calcium.6), making them a wonderful food for bone and cardiovascular function.
• Selenium (52.7 ug) — According to the article, the selenium in sardines supports immune health and promotes DNA repair. Your body also uses this mineral to create and recycle glutathione, your body’s “master antioxidant;” without enough selenium, your cells are left unprotected from damage.7
• Phosphorus (490 mg) and magnesium (39 mg) — Together with magnesium, these nutrients work to keep your bones mineralized and strong. They also stabilize your heart rhythm, support muscle contractions, and help your nerves fire correctly.
• Coenzyme Q10 — Although the quantity is not well-established, CoQ10 is also found in sardines. This compound is not only essential for mitochondrial energy production, but it also reduces oxidative stress, which contributes to fatigue and chronic disease.
One of the top advantages of sardines is that, unlike larger fish varieties like tuna or swordfish, they do not bioaccumulate high amounts of mercury. These make them a wonderful choice for people who need to be cautious about their exposure to this heavy metal, such as pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and young children.
“Unlike fish oil supplements, sardines provide nutrients in a whole-food form that is easily accessible and well-tolerated. The growing popularity of sardines reflects a shift toward natural, nutrient-rich options that promote long-term health,” News-Medical.net reports.8
What’s more, sardines beat processed meats for clean, lean protein. Compared to heavily processed meats like sausage, bacon, and deli cold cuts, sardines offer a cleaner, more efficient way to meet your protein needs without piling on harmful additives or excess polyunsaturated fats (PUFs).
Sardines Are Rich in Omega-3 Fats
Sardines offer some of the highest concentrations of omega-3 fats, specifically docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), among all seafood options. These healthy fats are good for your cardiovascular health, as they reduce inflammation, stabilize heart rhythms, lower blood pressure, and improve the quality of your blood lipids.9
• Why EPA and DHA are superior omega-3s — There are actually three types of omega-3 fats — these are EPA, DHA, and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). ALA differs from the two because it is sourced from plant-based foods. However, EPA and DHA surpass ALA in terms of their bioavailability. To put it simply, your body uses these two animal-based omega-3s more easily, allowing you to better reap their benefits.10
• Omega-3s play a vital role in cell membrane structure and function — They influence how your cells communicate and operate. Omega-3s maintain membrane flexibility, which is essential for various processes, including nerve function and immune responses. However, your body cannot produce these essential fatty acids, so you must obtain them through your diet.
• Omega-3 DHA boosts your brain health — DHA is a major structural component of the brain, essential for development in infants and children and for maintaining cognitive function throughout life. Research suggests potential benefits for memory, focus, mood regulation, and even reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.11
As for adults, one study notes that regularly eating sardines and other fish high in DHA were found to have healthy brain MRIs compared to people who consume fried fish or have a lower seafood intake.12
• Omega-3s from sardines are good for your heart — In optimal amounts (more on this later), omega-3s EPA and DHA offer significant heart benefits, such as reducing inflammation, supporting vascular health, and improving heart rhythm. An analysis published in the JAMA Internal Medicine journal notes:13
“[A] minimal fish intake of 175 g (approximately 2 servings) weekly is associated with lower risk of major CVD [cardiovascular disease] and mortality among patients with prior CVD but not in general populations. The consumption of fish (especially oily fish) should be evaluated in randomized trials of clinical outcomes among people with vascular disease.”
• Remember, you must get the right amount of omega-3s to reap its cardiovascular health benefits — Apparently, consuming too much omega-3s, particularly from supplements, is harmful as well, as it puts you at risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib),14 a type of arrhythmia that causes an irregular and often rapid heartbeat.
In fact, the relationship between omega-3s and heart health can be visualized as a U-shaped curve, where both deficiency and excess are detrimental. Learn more about this concept in my article, “The Omega-3 Paradox — How Much Is Too Much?”
However, by prioritizing your intake from whole food sources like sardines and other wild-caught fatty fish, and eating them in moderate amounts, you’ll sidestep this concern, since you’re getting omega-3s in their natural form along with other essential nutrients.
Other Health Benefits of Sardines
Sardines aren’t just for older adults or those who want to protect their heart health. They’re powerful for almost any age, as they help prevent disease, stabilize energy, and protect long-term health. Below are some additional benefits you could get when you add sardines to your diet:15
• Supports eye health — Regular consumption of DHA and EPA has been associated with a reduced risk of retinal disorders, including dry eye disease and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). If you’re constantly dealing with dry and irritated eyes, bumping up your sardine consumption will boost your tear production and reduce inflammation.16,17
• Helps promote healthy fetal growth — Since pregnant women are advised to manage their seafood consumption because of the mercury in many fish varieties, sardines is one safe option for them. Studies found that omega-3s in sardines and other fish provide vital support for fetal and infant neurodevelopment.18
• Boosts bone health — A 2023 study found that adults who consumed moderate amounts of healthy fats have improved bone mineral density. By consuming sardines, they will get moderate amounts of fatty acids to ensure sufficient bone mass.19
Eating 2 Sardines a Day Helps Keep Diabetes at Bay
Prediabetes is a condition in which your blood sugar level is too high, but not high enough for Type 2 diabetes. Today, 97.6 million American adults are dealing with this “invisible” condition — While you may not feel any changes, the damage is happening under the surface. Chronically elevated blood sugar quietly wears down your vascular system, creates inflammation, and reduces insulin sensitivity.
Sardines counter this by providing clean protein and essential minerals, and by supplying nutrients that support stable glucose metabolism. A 2021 study published in the Clinical Nutrition journal found that consistently consuming sardines may help protect against Type 2 diabetes.
• Researchers designed a study to test sardines’ effects — To conduct their experiment, the researchers enrolled 152 prediabetic adults at least 65 years old and placed them on a nutritional program aimed at reducing their risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. They were grouped into a control group and an intervention group.
• The intervention involved eating sardines with specific instructions — The intervention group was asked to consume approximately two cans of sardines in olive oil each week. The participants were given instructions to eat the entire sardine without removing the bones and were given a list of recipes.
• Sardine consumption significantly reduced diabetes risk — At the end of the year-long intervention, the researchers compared the risk of developing diabetes from the beginning of the study and the end of the study.
In the control group, 27% were at high risk of developing Type 2 diabetes at the start of the study, which dropped to 22% at the end of one year with nutritional changes. However, in the sardine group, 37% were at high risk of developing Type 2 diabetes before the intervention began. At the end of the year, this dropped to 8%.
• Additional health markers improved in the sardine group — The researchers also found there were other measurable parameters that improved in the group that consumed sardines each week. These included a reduction in insulin resistance, a rise in HDL cholesterol and an increase in adiponectin, a hormone that accelerates the breakdown of glucose. They also measured a decrease in blood pressure and triglycerides.
“Not only are sardines reasonably priced and easy to find, but they are safe and help to prevent the onset of Type 2 diabetes. It is easy to recommend this food during medical check-ups, and it is widely accepted by the population,” Diana D. Rizzolo, the study’s lead researcher, said.
“As we get older, restrictive diets (in terms of calories for food groups) can help to prevent the onset of diabetes … the results lead us to believe that we could obtain an equally significant preventive effect in the younger population.”
A Few Notes When Buying and Eating Sardines
Sardines don’t require refrigeration, they’re available year-round, and they’re incredibly versatile. You can add them to salads, sandwiches, and rice dishes. The flavor is bold, but when balanced with citrus, herbs, or tomato-based sauces, sardines become a savory, satisfying part of any meal.
• If you’re new to sardines, start small — Mix them into dishes where you’d normally use tuna, or mash them with mustard or Greek yogurt for a simple, nutrient-dense spread.20
• Fresh or canned? If you live in a coastal area and have access to fresh sardines caught locally, you’re in luck; they’re superior to canned varieties. Not only do they have a milder and sweeter taste, but they are also lower in sodium and have less nutrient loss as they are minimally processed.
• Fresh sardines require more preparation time — Look for fresh sardines that smell fresh (not fishy or stale). They should be firm to the touch, with bright eyes and a shiny skin.21 You’ll need to clean them properly before cooking them. The ones that you will not be cooking must be placed in the freezer immediately.
• Canned sardines are a more convenient option — If you don’t have access to fresh seafood, this is an ideal option. Canned sardines are already cooked and come in different varieties — packed in water, oil, tomato sauce, and even mustard. They have a long shelf life, and will last in the pantry for years.
• There are drawbacks to choosing canned sardines — For one, they could be high in sodium because of the liquid they’re brined in. Wash the sardines under cold water or remove the excess oil before eating. Canned sardines could also have bisphenol A (BPA), which may transfer from the can. To sidestep this, look for sardines sold in glass jars.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Sardines
Q: Why are sardines considered one of the healthiest fish to eat?
A: Sardines are rich in essential nutrients like omega-3 fats (EPA and DHA), high-quality protein, calcium, selenium, and vitamin B12. They provide whole-body support for heart health, brain function, bone strength, and immune balance — all in a clean, low-toxin form.
Q: Can sardines help prevent Type 2 diabetes?
A: Yes. A 2021 study found that adults with prediabetes who ate two servings of sardines per week had a dramatic drop in diabetes risk — from 37% to just 8% in one year — alongside improved cholesterol, insulin sensitivity, and reduced blood pressure.
Q: How are sardines better than other protein sources like bacon or deli meats?
A: Unlike processed meats that are loaded with saturated fat, additives, and inflammatory compounds, sardines offer lean protein with heart-protective omega-3s and no harmful preservatives. They also support energy, blood sugar control, and metabolic repair.
Q: Are sardines safe to eat regularly given concerns about mercury in fish?
A: Yes. Sardines are small, fast-growing fish that don’t accumulate mercury the way larger fish like tuna or swordfish do. This makes them a safer option for regular consumption, even for pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and children.
Q: What are some practical ways to add sardines to your diet?
A: Sardines are incredibly versatile — use them in salads, pasta, rice bowls, or spread them on crackers. If you’re new to the flavor, try mashing them with mustard or Greek yogurt. Choose BPA-free canned varieties or fresh sardines if available.