The silicon-integrated hole transport layer, crafted using microlithography, promises to power the next generation of VR, AR, and wearable devices with sharper images and greater energy efficiency.

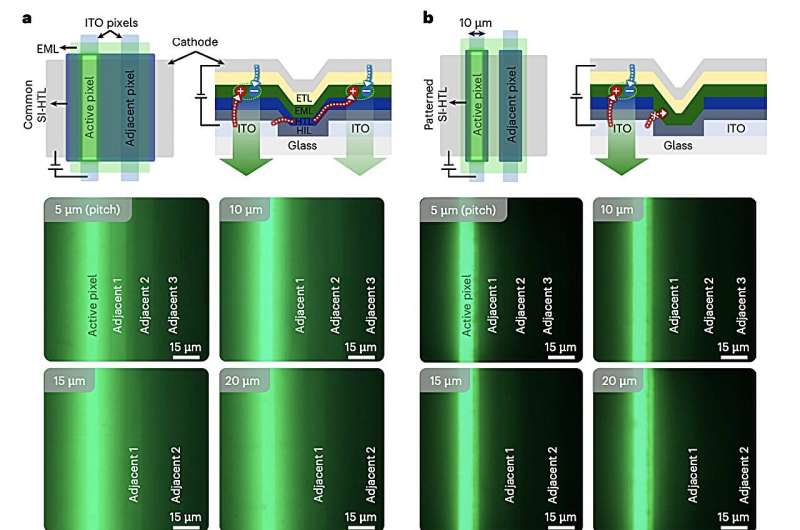
The rapid evolution of the electronics industry continues to push the boundaries of display technology. Among the most advanced and widely used display types are those based on organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). Unlike conventional liquid crystal displays (LCDs), OLEDs do not require a backlight, making them more energy-efficient. However, as pixel density increases, OLEDs suffer from a decline in image quality due to electrical crosstalk—unwanted interactions between adjacent pixels.
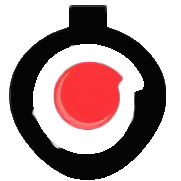
To address this challenge, researchers from Hanyang University, Yonsei University, and Sogang University in South Korea have introduced an innovative solution that enhances OLED performance without sacrificing energy efficiency. Their approach, detailed in Nature Electronics, involves integrating a silicon-based small-molecule hole transport layer (SI-HTL) using microlithography, a precise patterning technique widely used in semiconductor fabrication.
“High-density displays are essential for next-generation VR and AR devices,” wrote researchers Hyukmin Kweon, Seonkwon Kim, and their team. “However, increasing pixel resolution often leads to greater electrical crosstalk due to shared hole transport layers. We demonstrate that a silicon-integrated small-molecule hole transport layer, patterned at the wafer scale, can significantly mitigate this issue.”
By leveraging microlithography, the researchers successfully fabricated micro-patterned OLED arrays and tested their performance. Their findings revealed that the new SI-HTL structure significantly improved charge balance, resulting in enhanced luminance and reduced crosstalk. The team achieved an ultra-high resolution of 10,062 pixels per inch (PPI) on a six-inch wafer while maintaining strong energy efficiency.
This opens new doors for high-definition OLED displays, particularly for VR and AR applications, smart glasses, wearables, and next-gen smartphones. With improved pixel resolution and reduced power consumption, this technology could play a vital role in shaping the future of immersive digital experiences.